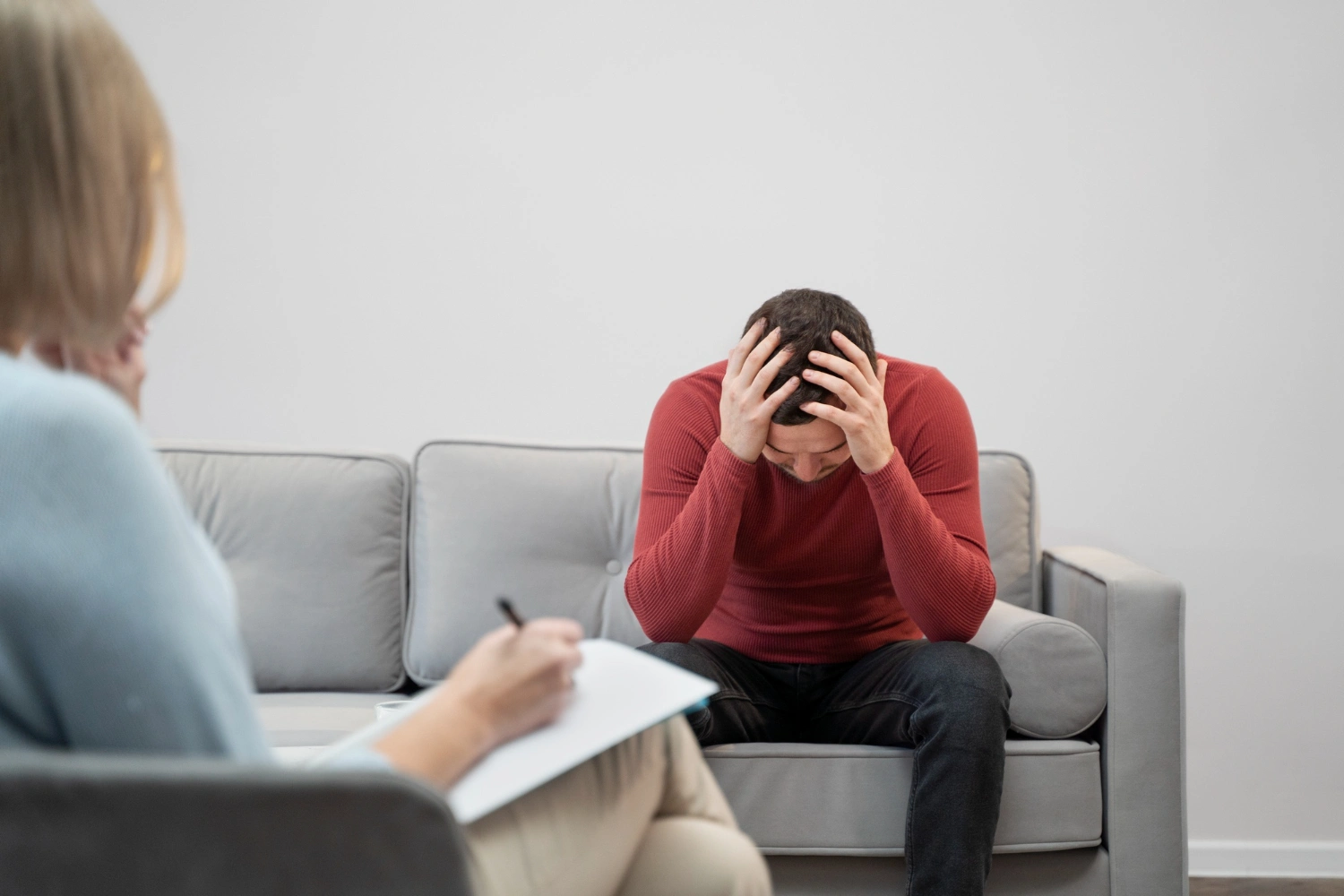
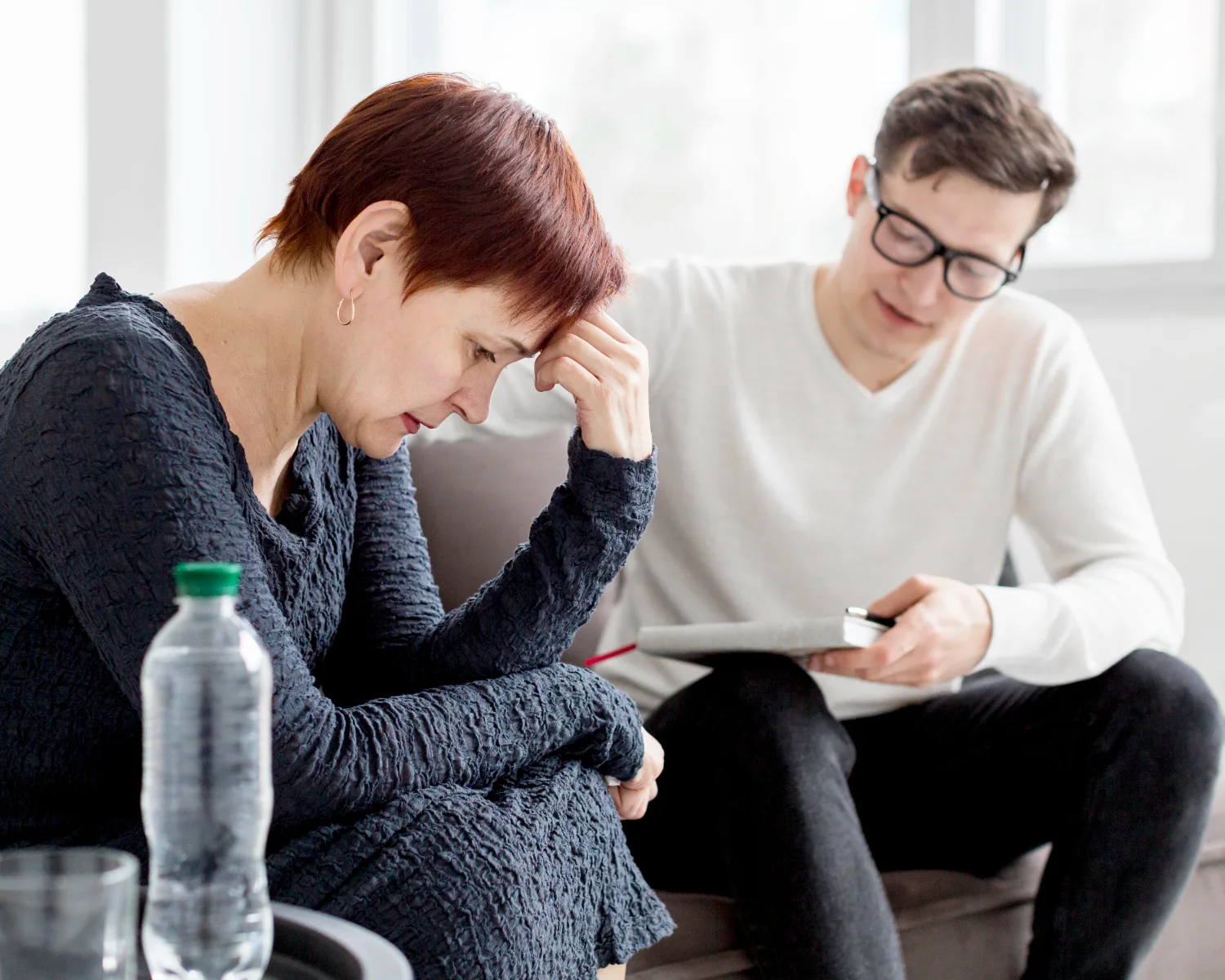
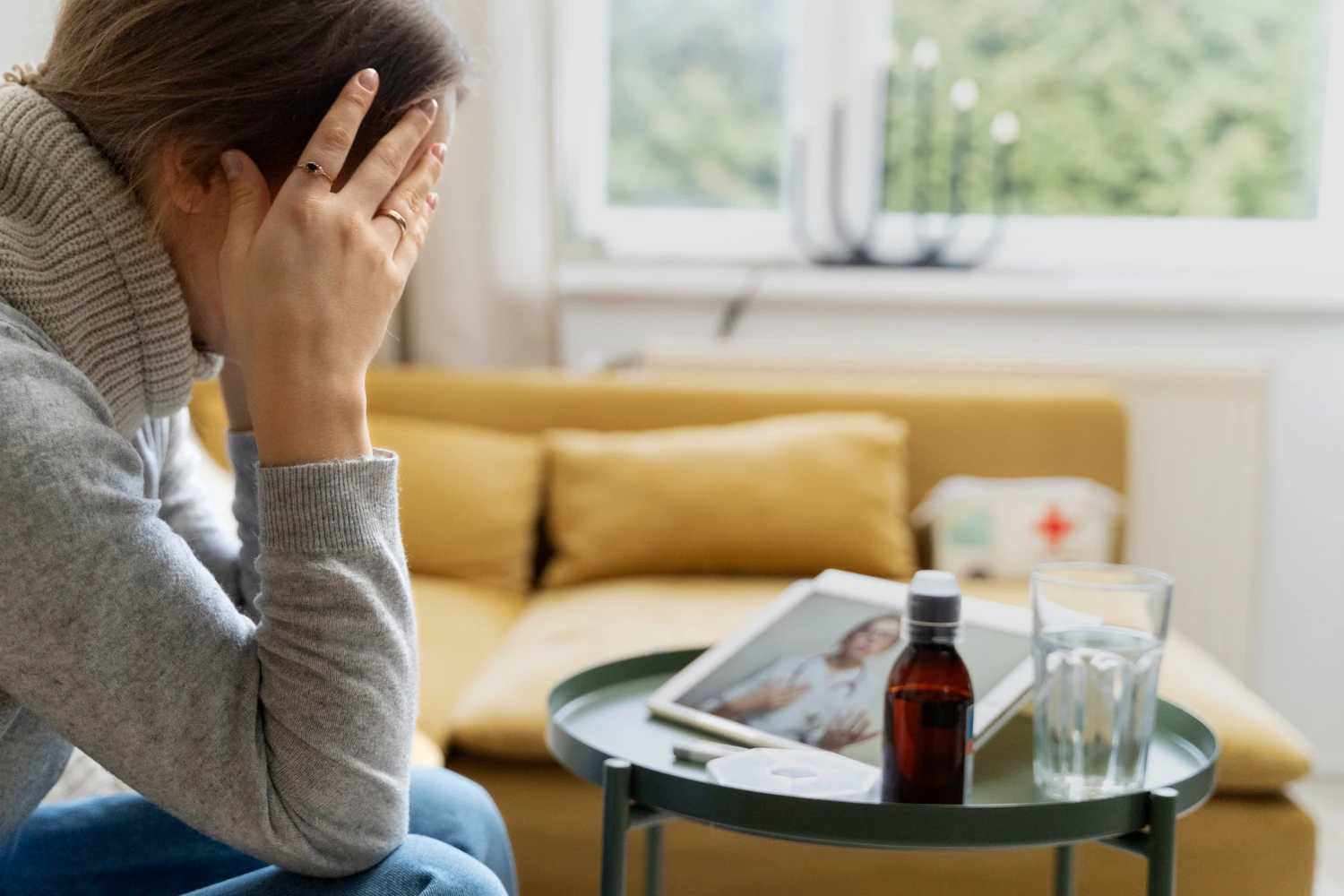
People with depression often report low energy, a diminished interest in or enjoyment of activities, and difficulty completing tasks or solving problems. Avoiding potentially enjoyable or rewarding activities can make these symptoms worse. This can create a vicious cycle where a person’s reduced participation in fulfilling activities leads to even less interest, lower mood (feelings of sadness and despair), and heightened feelings of helplessness or worthlessness. As a result, the person becomes even more disengaged from activities they once found pleasurable or productive, which further worsens depressive symptoms. Over time, this downward spiral can continue until the person believes they are incapable of experiencing pleasure, finishing tasks, or solving problems. In the most severe cases, individuals may lose all hope and abandon any efforts to change. Fortunately, depression is treatable with a combination of therapy, lifestyle changes, nutritional medicine, sometimes medication, and ongoing support. Seeking help is an important step toward recovery and improving quality of life.
Signs and Symptoms of Depression
-
Feelings of sadness, tearfulness, emptiness or hopelessness
-
Angry outbursts, irritability or frustration, even over small matters
-
Sleep disturbances, including insomnia or sleeping too much
-
Tiredness and lack of energy, so even small tasks take extra effort
-
Slowed thinking, speaking or body movements
-
Feelings of worthlessness or guilt, fixating on past failures or self-blame
-
Loss of interest or pleasure in most or all normal activities, such as sex, hobbies or sports
-
Frequent or recurrent thoughts of death, suicidal thoughts, suicide attempts or suicide
-
Reduced appetite and weight loss or increased cravings for food and weight gain
-
Trouble thinking, concentrating, making decisions and remembering things
-
Unexplained physical problems, such as back pain or headaches