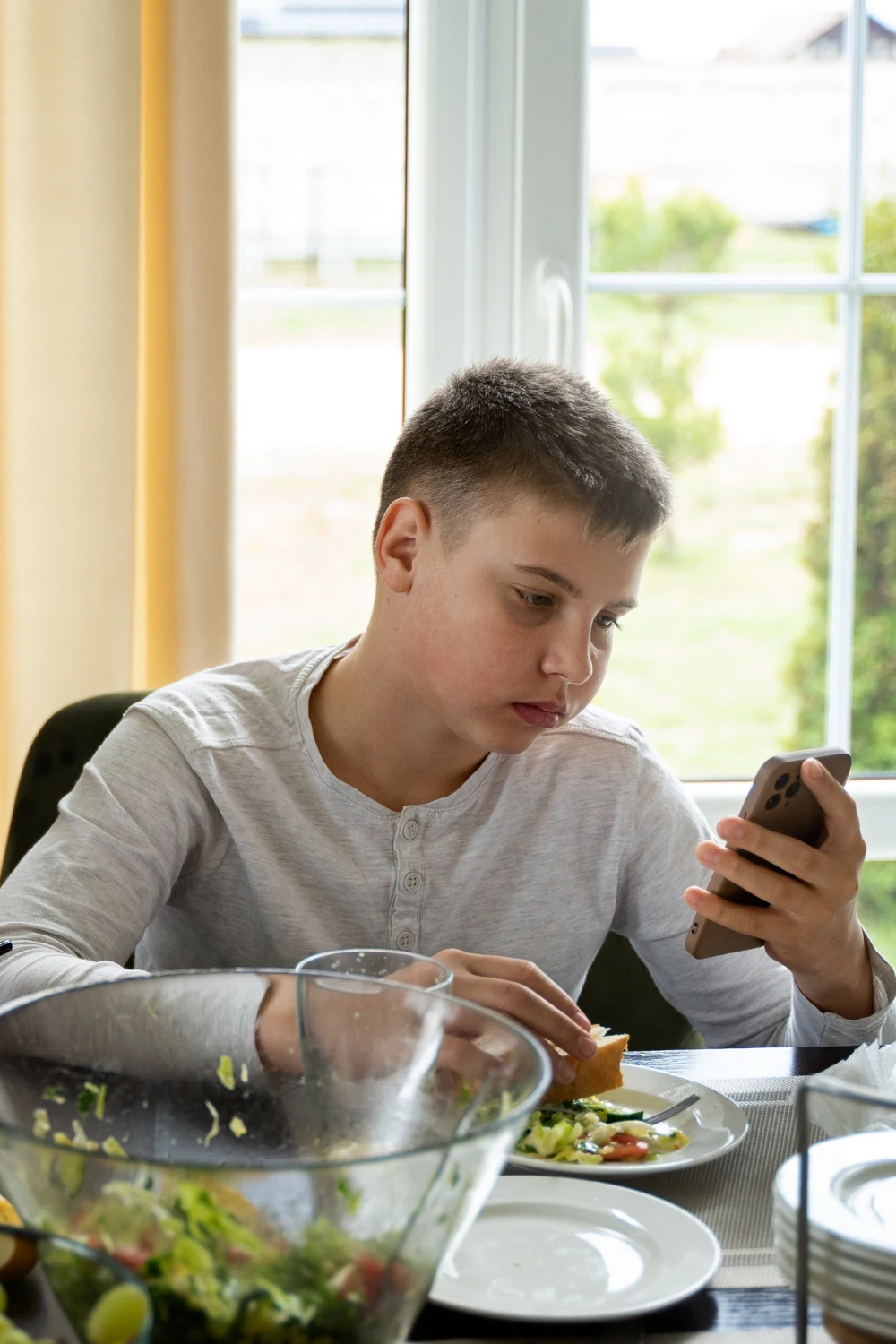
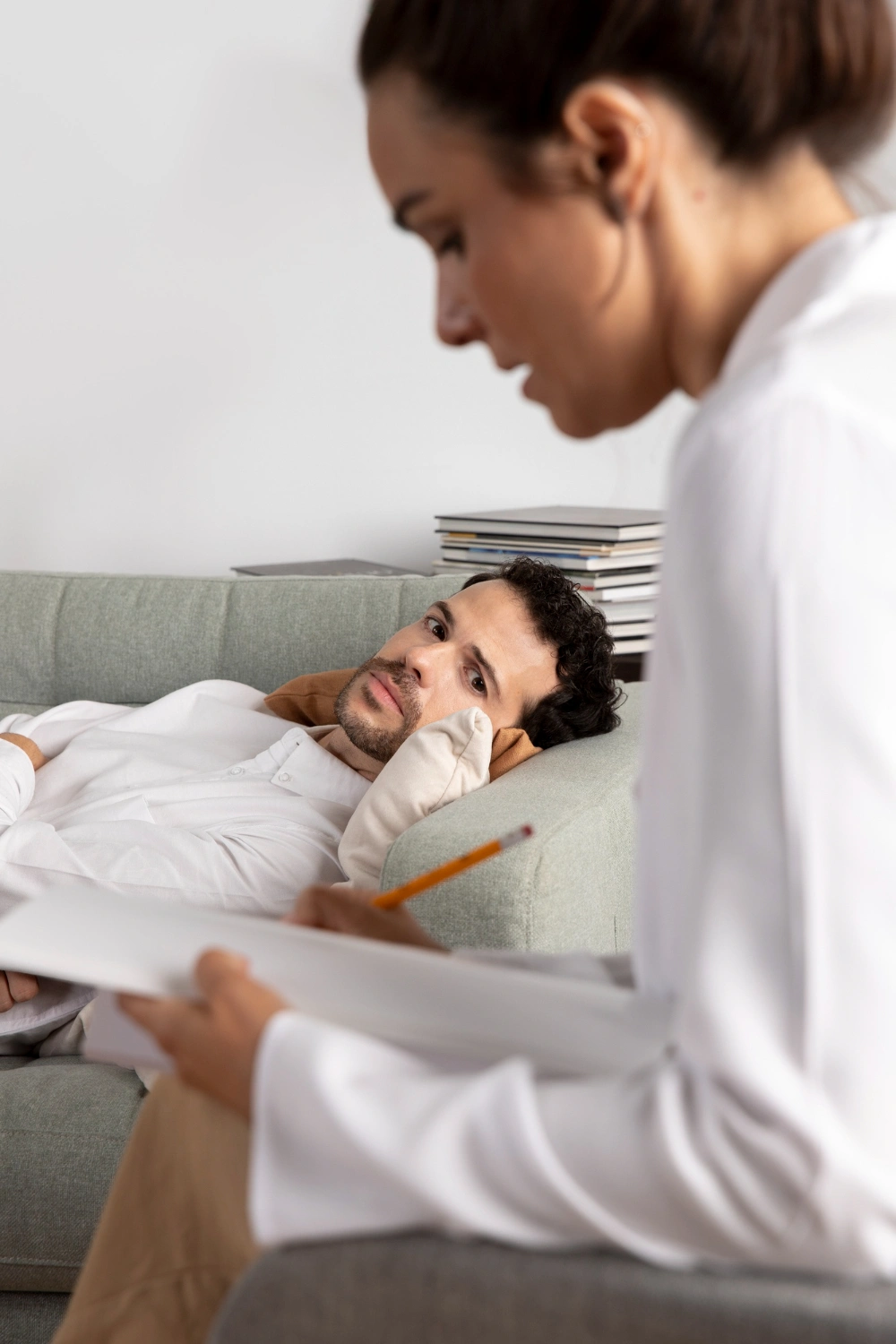
Stress refers to any internal or external stimulus that triggers a biological response. The body’s reactions to these stressors are known as stress responses. Depending on the nature, timing, and intensity of the stimulus, stress can have various effects on the body, ranging from changes in homeostasis to potentially life-threatening consequences, including death. Chronic stressors encompass everyday challenges such as traffic jams, work overload, financial struggles, marital disagreements, children or family issues. While there are many other potential sources of stress, these are the most commonly experienced in daily life. Stress can both trigger and exacerbate numerous diseases and pathological conditions. Chronic stress is considered a major risk factor for lower quality of life and premature death, accounting for 75%-90% of all visits to family physicians. Studies indicate that nearly every system in the body can be affected by chronic stress. When stress is not alleviated, it weakens the immune system and eventually leads to illness. One can only imagine the consequences if the body were to stay in a constant fight-or-flight mode.
Signs and Symptoms of Stress
-
Headaches
-
Fatigue
-
Sleep disturbances
-
Muscle tension
-
Digestive issues
-
Changes in appetite
-
Irritability or mood swings
-
Anxiety or nervousness
-
Reduced concentration
-
Increased heart rate or palpitations